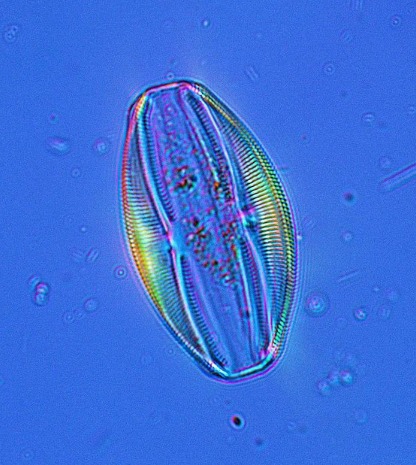
In a world grappling with the challenges of climate change, an unsung hero—diatoms has emerged as a natural solution in a fight against climate change.
This tiny but remarkable organism quietly played a vital role in shaping earth’s destiny in the past when the planet experienced a tumultuous period of extreme cold some 150 to 200 million years ago.
Diatoms, a type of algae, play a vital role as primary producers in aquatic ecosystems, maintaining the delicate balance of our planet’s waters. Through the process of photosynthesis, these microscopic powerhouses utilize sunlight, carbon dioxide, and nutrients to fuel their growth.
But their significance goes beyond their role as aquatic architects. Diatoms possess a remarkable ability to absorb atmospheric carbon, effectively removing it from the air we breathe. What sets them apart is their exceptional efficiency in carbon storage. These minuscule organisms have evolved intricate silica cell walls that not only provide structural support but also serve as repositories for captured carbon.

Scientific studies have delved into the realm of diatoms and their impact on carbon sequestration, shedding light on their invaluable contributions to unlocking the potential of biomass resources. A noteworthy 2020 study titled “Wealth for Waste: Diatoms as Tools for Phycoremediation of Wastewater and Obtaining Value from Biomass” explored the possibility of using diatoms as agents for wastewater treatment while extracting value from their biomass.
Another recent study in 2022, “Carbon Sequestration Potential in the Restoration of Highly Eutrophic Shallow Lakes,” demonstrated the effectiveness of diatoms in restoring and improving highly eutrophic shallow lakes. By reducing nutrient levels and enhancing water quality, these organisms prove to be valuable tools for managing and restoring eutrophic aquatic ecosystems.
To further emphasize the significance of aquatic organisms in climate regulation, consider the Azolla event that took place around 50 million years ago. During this period, the floating water fern Azolla experienced exponential growth, leading to the sequestration of substantial atmospheric carbon and contributing to a cooler climate state. This historical event highlights the shared potential of aquatic organisms, including diatoms, in climate regulation throughout Earth’s history.
Nature-based solutions, such as diatoms, are now emerging as promising approaches in the battle against climate change. Not only do diatoms sequester carbon, but they also enhance water quality, promote biodiversity, and contribute to the overall health of aquatic ecosystems. By raising awareness about the historical significance and relevance of diatoms, we can instill awe and curiosity, fostering a newfound appreciation for these unsung heroes of the natural world.
The extraordinary potential of diatoms in mitigating climate change calls for collaboration among scientists, policymakers, and environmentalists. Through collective efforts, significant opportunities for carbon removal can be unlocked, paving the way for long-term climate solutions. With the urgency of the climate crisis, it is crucial to take collective action and commit to preserving our planet for future generations.
If you are interested in supporting or collaborating on initiatives related to diatoms and climate change, please reach out to us at rhizosolenia.collaborate@gmail.com. Together, we can make a difference and shape a sustainable future for all.
Thank you for joining us on this journey into the captivating world of diatoms and their vital role in maintaining our planet’s ecological balance. Stay tuned for more installments in our four-part series, as we continue to explore the fascinating contributions of diatoms.